Solar Farms: Everything You Need To Know

Declared as the best renewable energy source in terms of minimal pollutants and cost-efficiency, solar energy has become a rage among enthusiasts of energy resources.
Since solar energy has been hugely popularized in the energy resource market recently, it is time to look at the various ways to get the best out of solar energy regarding financial and environmental concerns.
A great way to do this is to consider solar farms – an amazing way of getting all the benefits of solar energy but on a larger scale. Here, you will find a guide on everything you need to know about solar farms, and why it’s the new goldmine in terms of energy resources.
With solar farms, not only can you reduce your carbon footprint while generating power, but it proves to be a financial asset in the coming years. Let’s first see what a solar farm is and how it works.
- 1. What Is A Solar Farm?
- 2. How Do Solar Farm Work?
- 3. Types Of Solar Farms
- 4. Solar Farms Pros and Cons
- 5. Are There Health Risks of Living Near a Solar Farm?
- 6. What Should Be Considered To Establish A Solar Farm?
- 7. What Is The Largest Solar Farm In The World?
- 8. How Much Does A Solar Farm Cost
- 9. Conclusion
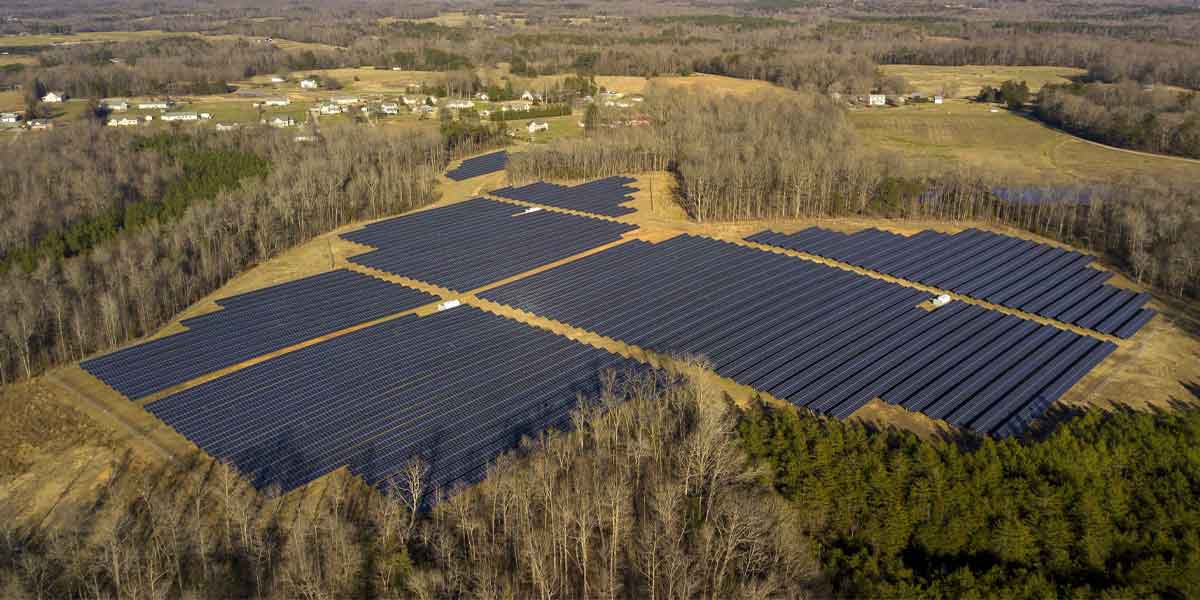
What Is A Solar Farm?

Whatever you may prefer to call it – photovoltaic solar farms, photovoltaic power stations, or even solar parks – they’re all names talking about a project about a large-scale solar energy setting that converts energy received from the sun into electricity.
Whether this is done for the consumption of households and residential purposes or whether it will be utilized in a more practical and commercial setting – the basic idea behind these solar farms is energy conversion.
While we’ll see, in detail, what the two major types of solar farms are and what they’re typically used for, the bottom line for both of them is that they’re mainly established as numerous photovoltaic or solar panels installed on open ground to allow for maximum absorption of sunlight.
Let’s see how this works and how these large-scale solar projects are the upcoming powerhouse for the utilization of renewable energy.
How Do Solar Farm Work?
Now that you know the basic idea behind the rise of solar farms in recent years, it is essential to see why exactly they work so well. As you know, these solar farms involve large areas that have solar panels installed onto them – and these solar panels are responsible for absorbing sunlight as much as possible, which is denoted by solar energy.
This solar energy is then converted into electrical energy, which can then be sent to power grids to be utilized by large firms or large households. Essentially, the idea behind solar farms is the same as individual solar panels that are installed on rooftops – just on a larger scale.
Types Of Solar Farms
Owing to the versatility of solar farms, they can either be used as utility solar farms or community solar farms. Since these photovoltaic panels are essentially able to produce large amounts of energy to supply to power grids, they can either be used for comparatively smaller or even larger projects.
1. Utility Solar Farms
The word “utility” suggests that these solar farms mainly send their generated energy to the utility company in the area. However, that is true for all solar farms – no matter what scale they might be on.
For this purpose, utility solar farms are traditionally referred to as those photovoltaic projects that are extremely large-scale and use a huge number of solar panels to supply energy directly to the high voltage grids and then to households or commercial organizations.
2. Community Solar Farms
The main difference between utility solar farms and community solar farms is that the latter is significantly smaller. These community solar farms are mainly set up in an area that gets the maximum amount of sunlight, generating solar energy to supply to all the houses and farms in the neighborhood.
Individuals and owners of commercial organizations can join these solar energy programs to be a part of the recipients of the solar energy through the larger electricity grid that powers the entire neighborhood – and will thus have their energy bills adjusted accordingly. Hence, community solar farms are set up to transfer energy for close-range recipients only.
Solar Farms Pros and Cons
In the next section, we will be discussing the pros and cons of solar farms, after you have read the pros and cons, you can decide whether you want to invest in a solar farm.
Pros of Solar Farms

1. Requires Less Maintenance
Solar farms are popular for minimal maintenance. After installing these photovoltaic or solar panels on the farms, they can last you around two decades without much fussing or maintenance check-ups.
All you will have to do is clean your solar panels twice a year – but apart from that, there’s not much you have to do in terms of maintenance in solar farms. As opposed to wind turbines, solar farms require lesser maintenance.
2. Zero Emissions
Solar farms are highly environmentally friendly, meaning that they can create almost no harmful emissions for you for the duration of their installation. They can, however, create minimal amounts of emissions owing mainly to the usage of petroleum in the making of the photovoltaic panels.
However, this is only a one-time emission cost – as opposed to other sources of energy, which result in continuous emission costs. This results in a comparatively more eco-friendly energy resource.
3. No Power Interruption
Since solar farms are powered based on a renewable energy source, essentially the sun, you can rest assured that solar energy will not fizzle out any time soon. Additionally, during the day, solar farms can function without interruption if it receives enough sunlight instead of other energy sources that may malfunction and stop working due to various reasons.
You can count on solar energy to be functioning as long as you have adequate sunlight – which is most of the time anyway.
4. Creates Employment
Lastly, solar farms are sustainable for the environment and are also hugely responsible for causing a job employment boom in related services. For jobs pertaining to solar energy farms, such as solar panel installation, many more vacancies are created, which automatically points towards rural and urban development in terms of job creation.
Since renewable energy has begun to be popularized recently, employment opportunities can be seen as rising.
Solar Farms Disadvantages

1. High Downtime
It is a popularly known fact that solar panels (may be polycrystalline or monocrystalline) can only derive their energy as long as the sun is in the sky. At night time, while energy can be saved and stored for usage after sundown, it is still not as effective as solar energy directly from the sun.
Additionally, various other issues, such as weather conditions, may influence your availability of solar energy quite a bit. The downtime of available solar energy becomes high.
2. Expensive To Build
In terms of solar farm disadvantages, this one is perhaps the most striking. The initial costs of installing solar panels over a large stretch of land can be pretty high. The average cost of a single megawatt of solar panels is around $3 million – an astronomical amount, even if it is funded by the entire neighborhood or by a large capital organization.
While the costs after a few years can often cover the initial costs of installation, it is impractical for an average neighborhood collective to garner this amount to allow for a community solar farm.
3. High Energy Storage Cost
As mentioned before, since solar energy cannot be supplied constantly throughout the day owing to the hours after the sun has set, it is necessary to invest in some storage facility that will be responsible for storing any excess amount of solar energy for use after sundown.
A battery, for example, can be quite expensive – no matter the price range you’re seeking.
4. Takes Up A Lot Of Space
As you might know by now, solar farms can only be established over extremely large and empty areas that fit the installation of hundreds and thousands of solar panels.
It might be pretty difficult looking for a space like this with other spatial considerations in mind, such as weather conditions, proximity to residential spaces, and such. Since such enormous land area stretches are required for solar farms, they’re mostly established in rural areas.
Are There Health Risks of Living Near a Solar Farm?
The entire process of production of electricity from solar energy and its transmission to the power grid (on a scale as large as a solar farm) does indeed emit weak electromagnetic fields. However, extensive studies and research in this regard have proven that exposure to such tiny levels of electromagnetic fields has no negative effect on human health. (Refer more on this here.)
What Should Be Considered To Establish A Solar Farm?
If you’re considering solar farms’ pros and cons with relation to establishing your very own solar farm, then remember to keep a few things in mind as the primary components of “how to build a solar farm.” Knowing your land and how suitable it is in holding large numbers of photovoltaic panels is the first step in narrowing down the area where you’re planning to establish your solar farm.
Additionally, you will need to keep in mind extraneous factors such as how suitable your land is for establishing a solar farm and what weather conditions you can anticipate in the area – and if they’ll interfere with the working of the solar farm.
Lastly, maintenance and installation costs are significant logistical concerns that must be kept in mind. If you want to go through a more detailed account of establishing your own solar farm, you can do so by reading the linked article.
What Is The Largest Solar Farm In The World?
The largest solar farm in the world is located in Rajasthan, India, and is referred to as the Bhadla Solar Park. Stretching over a span of around 14,000 acres, the overall capacity for solar energy harnessed by the Pavagada Solar Park is 2245 megawatts.
As said, it spreads over an extremely large area – and is the size of an entire town. Owing to its size and sheer magnitude, the Bhadla Solar Park is referred to as a solar farm instead of solar gardens, which are more commonly used to denote smaller and more residentially-driven solar projects.
How Much Does A Solar Farm Cost
In short, your solar farm can cost you anywhere from $1 to $4 million per megawatt of solar energy that you’re going to be harnessing, depending on the type of solar farm that you’re looking to establish. If you’re planning to go for a utility solar farm, then installation costs per megawatt can be around $1 million.
As you might know, a single megawatt of harnessed solar energy can power around 200 households – and this is the minimum requirement for a potential utility solar farm.
For community solar farms, the needs are bound to be fewer; however, they can cost around $2 to $4 million per megawatt. All these should solve your solar farm related questions, if you have more solar related questions check out our post on popular solar questions.
Conclusion
Solar farms are argued by many to be the need of the hour – and while it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages, the pros far outweigh the cons in the long run.
When it comes to sustainability and paying over the installation costs in the future, solar energy is at the top of the chart, which makes it only natural that they should be installed on a large-scale to provide its benefits to more households and organizations and make renewable energy more accessible to everyone.
Now that you have a brief overview of all issues related to solar farms, it is time to take a step in the right direction with them!