Popular Solar Panel Questions Answered

Going solar is never usually an impulsive buy but a calculated decision. Most homeowners across the globe consider switching over to solar energy systems as an expensive choice. Although it may be one of the largest purchases that a person will make in their lifetime, it’s worth it.
Speaking of that, it usually takes homeowners a lot of thinking and calculations before investing in a solar energy system and a lot of effort and determination to put it all together once decided.
However, one of the major drawbacks is that many people are genuinely unaware of the major complexities of the solar industry, which generally compel them to opt out of choice for adopting solar energy systems.
Therefore, going further through this article, anybody will be able to learn about some of the basic yet significant questions that a person should know while considering solar energy systems. Hence, keep on reading to clear your confusion and answer your curiosities.
-
1.
Solar Panel FAQs
- 1.1. 1. Why Should You Go Solar?
- 1.2. 2. How Do Solar Panels Work?
- 1.3. 3. How Are Solar Panels Affected By Cloud And Rain?
- 1.4. 4. What Are The Components Making The Solar Energy System?
- 1.5. 5. What Is The Difference Between Grid Tied And Off Grid Solar?
- 1.6. 6. Can Solar Power Be Stored?
- 1.7. 7. How Many Solar Panels Do You Need?
- 1.8. 8. What Is A Solar Power Inverter?
- 1.9. 9. Why Is Solar Power Not Popular?
- 1.10. 10. Can Solar Power Run Air Conditioners?
- 1.11. 11. Can Solar Power Charge Electric Cars?
- 1.12. 12. Do Solar Panels Overheat?
- 1.13. 13. What Type Of Solar Panel Should You Buy?
- 1.14. 14. Can Solar Panels Be Recycled?
- 1.15. 15. Will Solar Panels Work After An EMP?
- 1.16. 16. What Is Net Metering?
- 1.17. 17. Will Solar Panels Save You Money?
- 1.18. 18. Will Solar Power Become Cheaper?
- 1.19. 19. How Should You Finance Your Panels?
- 1.20. 20. Are Solar Panels Worth The Money?
- 2. Conclusion
Solar Panel FAQs
1. Why Should You Go Solar?
To begin with, many people have this common question: Why is solar power good? Perhaps to answer that, it depends on the person and his/her decision of whether they want to switch over to solar energy or stick with the conventional energy system. The principal reason why most homeowners opt for solar energy is to save or reduce their electricity bills.
Solar power also enables an individual to increase their property value. In many places, solar system owners are also paid for excess energy that their panels usually produce.
Other reasons for opting for a solar energy system include reduced carbon footprint, more job opportunities, promotion of the future of renewable energy, etc. Despite all of these positives, there are a few possible danger you can face with solar panels, you should read about them before planning to buy solar panels.
2. How Do Solar Panels Work?
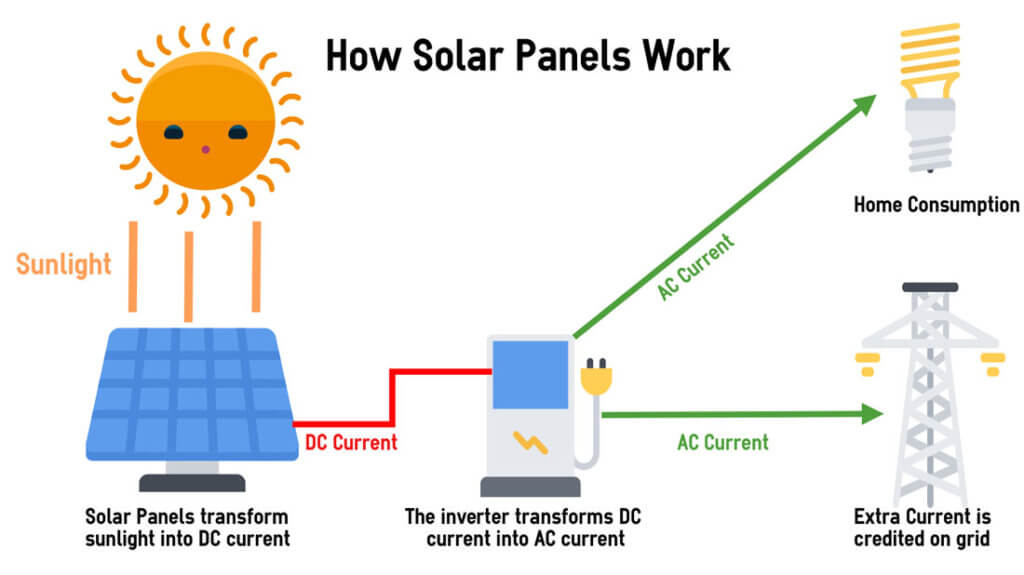
There are many solar power advantages, and solar systems usually generate power from direct sunlight. The panels in the system use sun exposure to produce electricity by converting the sunlight into direct current or DC energy.
Additionally, most appliances in a house are generally connected to alternate current or AC power which screams for the effort of connecting the solar panels to an inverter. This inverter, thus, changes the required solar energy from DC to AC.
A popular misconception about solar energy is that it’s difficult to regulate the entire electricity bill since solar power does not produce anything during night hours. However, many services provide a professional installation that helps to size the system accordingly, to produce enough power during daylight to offset all of the usages.
This, in return, helps to store the excess energy. When the system is not producing any solar power during night hours, the power put on the grid offsets the amount one takes off.
Therefore, it means that even if the solar system is not producing any power at night, it has the capacity to produce a sufficient amount of power during daylight. Also, while solar panels may be less efficient on days with bad weather, they do still produce enough electricity to suffice the requirements for the day.
3. How Are Solar Panels Affected By Cloud And Rain?
This is yet another myth about the solar energy system that it’s unable to produce any power when it’s cloudy or raining. As we learned briefly in the previous section, solar power may be less effective on bad weather days. Still, solar panels can produce up to 25% of their typical power output regardless of cloudy weather.
In case it’s raining heavily, solar panels can still produce about 10% of their regular power output. Interestingly, during consistent bad weather events, the solar panels can actually draw upon their previously stored energy, making the home completely off-grid.
4. What Are The Components Making The Solar Energy System?
The main components of grid-tie solar systems are:
- Racking: refers to the foundation on which one mounts their system.
- Solar Panels: to trap sunlight during the day. (Monocrystalline And Polycrystalline)
- Inverter: to convert solar energy from AC to DC.
- Whereas battery-based systems also include:
- Charge Controllers: used to control the rate at which batteries charge from solar.
- Batteries: used to store the energy that is generated.
These systems also include meters, disconnects, and wires.
5. What Is The Difference Between Grid Tied And Off Grid Solar?
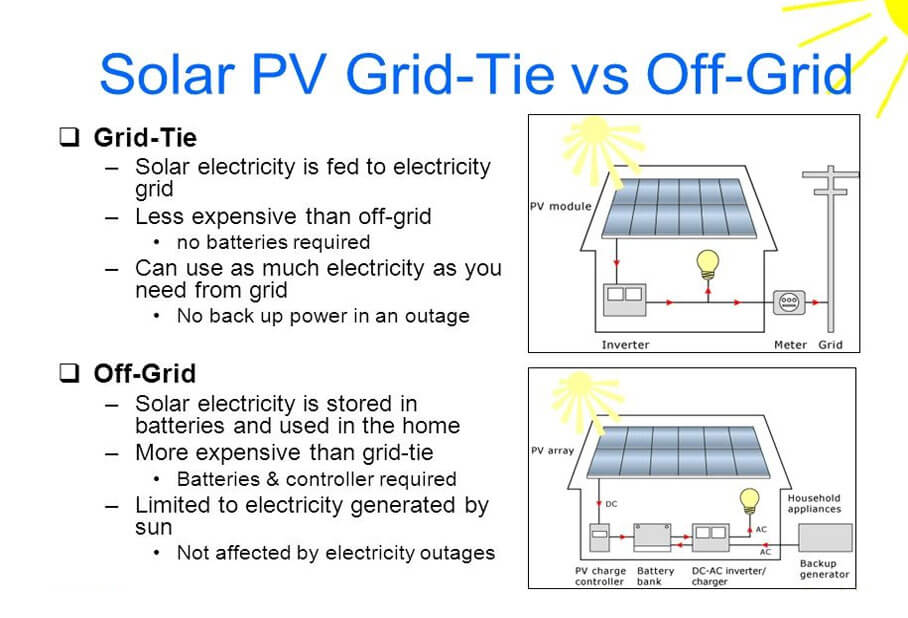
A grid-tie solar system connects to the public utility grid, which acts as extra storage for the excess energy produced by the solar panels to avoid investing in purchasing new batteries. This is a great way to save money effectively and hence, is a much-recommended suggestion.
If a person does not have any access to power lines at their residence, they may opt for an off-grid solar system with batteries that help store energy for later usage.
Apart from these two, there’s a third kind of solar system, called grid-tied with energy storage. These usually connect to the grids and also include batteries for power backup in case of power cuts.
6. Can Solar Power Be Stored?
To answer that simply, yes, solar power can be stored in batteries. This is usually seen in grid-tie solar systems with battery backups and off-grid solar systems. The solar panels basically convert the sun’s energy into DC power, and the batteries store the power for further usage. Therefore, this creates the ability to operate independently of the utility grid.
Although this may sound very interesting in theory, it’s quite a big deal for the vast majority of customers as well as impractical. To estimate all the solar systems installed across the globe every year, less than 1% of them actually utilize battery technology for solar energy storage.
Well, there’s no denial that batteries are indeed very expensive and also unreliable for some residences. It is because large electrical appliances like air conditioning, water heating, and washers generally require much more power than the capacity of these batteries. Thus, most people use an alternative method in which the solar system is connected to the grid.
Henceforth, in this way, the energy is used by the residence, and the excess power flows back to the utility grid. The utility grid keeps track of the amount of energy traveling back, which is also referred to as net metering.
7. How Many Solar Panels Do You Need?
One of the most common questions that people frequently ask is that how many solar panels will suffice in switching over to self-sustaining solar power? Well, to answer that fairly, there are a lot of factors that usually depend on that.
For example, the efficiency of the solar panels that are being opted for, the amount of power used each month, etc. For a home that uses about 5kW power each month, an average of 20 solar panels would easily suffice. Additionally, 300 square feet of roof space, ideally facing the south, will be required for the solar panel installation.
8. What Is A Solar Power Inverter?
While many of you may be clear about solar panels and their functionality up till now, there may be confusion regarding what a solar inverter is or how it typically works. To put it in simple words, a solar inverter is considered the brain of the operation of solar systems.
Its principal task is to convert the sun’s energy from DC to AC power so that your house can accommodate the form of electricity produced by solar panels. Thus, the inverter also communicates with the electrical grid to keep the energy in sync. It also automatically shuts down in case the grid goes down.
9. Why Is Solar Power Not Popular?
Now, you may be wondering, “If solar power is so good, why is it not popular enough?” It all usually drains down to one primary reason behind it: the cost. Up until the recent past, solar power was not very cost-effective for everyone, especially people with average financial conditions.
This forced many people to tone down their interests and curiosity to purchase a solar power system and continue with their traditional systems.
The cost of an average solar power system was much higher and expensive 20 years ago in comparison with today’s price ranges. For instance, a solar power system worth $15,000-$25,000 might have cost someone around the estimate of $100,000-$150,000. Therefore, the price difference is visibly huge, and many people could not afford such luxuries.
However, another notable big change occurred when the availability of financing mechanisms to provide help to the regular people increased.
This choice lets the customers plan their finances before going solar, and instead of issuing a check for thousands of dollars, invest an organized plan to install their solar power system. This also helped the customers to reduce their monthly electricity bills.
Hence, the following changes have made the solar power system available to the average person and expanded the target audience for various companies.
Thousands of people are switching over to solar power nowadays to reduce the hassle of handling increased electricity bills. Read more about the pros and cons of Solar Panels in this article.
10. Can Solar Power Run Air Conditioners?

So, air conditioning is considered one of the largest electrical appliances in a home. It is also most likely to be the sole factor responsible for your higher electricity bills during summers. It is because of the huge electrical demand that almost every air conditioning unit requires to function.
Solar power can actually provide a huge load of electricity, provided there is a big enough solar system installed for fulfilling the requirements. Large-scale businesses usually require 3-phase power to utilize solar to satisfy their solar energy needs.
With a grid-tied solar system, the amount of energy produced by the solar system is transferred to the already existing electrical system.
Therefore, solar power can actually provide energy to run an air conditioner. If you want further help with running some numbers, we have a dedicated post to help you with the number of solar panels required to run an air conditioner.
11. Can Solar Power Charge Electric Cars?
Yes, you can charge your electric cars with solar power. There are quite a few different ways to do that without the involvement of duct-taping huge solar panels on the roof of the car.
Electric cars simply allow you to plug the solar power into an outlet to charge at your home conveniently. For that to happen, the only thing you’d require is to install a grid-tied solar power system at your home.
This will ensure you have the option open for charging your electric cars through solar power and your entire house if the need arises. Charging the electric car at night will ensure the power is flowing from the utility grid to suffice the need of solar power.
Another way to invest in an electric car is by opting for a solar car charger unit.
12. Do Solar Panels Overheat?

Solar panels absorb direct sunlight to produce energy. However, an important question that may pop up in your mind is: How much sun is too much? Many panels operate with less efficiency in extreme sunlight, whereas others are usually the most efficient around maximum sun exposure.
Therefore, upon studies and experiments, it is suggested that solar panels lose a certain amount of efficiency for every degree above 77 degrees Fahrenheit. Thus, this is known as the temperature coefficient figure.
A person may need to select solar panels with a better temperature coefficient for someone living in the desert. For instance, thin-film solar panels are known for their ability to work efficiently in hot temperatures.
On that note, you may want to remember that solar panels don’t stop functioning even when they get hot; however, their efficiency might take a hit. Study more about the effect of heat on solar panels in this blog by SolarReviews.
13. What Type Of Solar Panel Should You Buy?
Solar panels are ever-evolving in size, power production, and efficiency, which make it difficult to choose one from the varieties available on the plate. Another thing to mention is that people mostly go for the aesthetics of how the system appears to be rather than its functionality.
Solar panels are classified as these three basic types – monocrystalline, polycrystalline and thin film panels. EnergySage explains in great detail, how these differ from each other and which should you prefer based on your requirements and other factors at play.
As far as brands are concerned, Jinko, Heliene, Longi, Trina, Tesla, etc., offer the best quality products. Remember, all solar panels must have a Kilowatt-hour or kWh number listed with them to indicate the amount of power the panel will produce per hour in the sun.
14. Can Solar Panels Be Recycled?
Well, here’s the thing. While you may be wondering if solar power is good for the environment since you’re about to make the switch or are genuinely interested, the good news is that solar power systems and solar panels are recyclable. The Environmental protection agency states that the contents of standard solar panels are fairly recyclable.
Solar panels usually last up to 30 years and more, depending upon care and maintenance, which make them convenient and overall a better option. Therefore, you won’t be required to change them anytime soon, once they’re installed.
However, the rules of recycling may be quite pertinent to some people. The EU has a more proper and organized system for recycling, whereas the US offers the opposite.
15. Will Solar Panels Work After An EMP?
So, can a solar power system work even after an EMP blast? To be honest, nobody really knows. It’s because there have not been any reports of a large-scale EMP blast before. However, factors like the strength of the EMP blast and the location will play a major role in case of a sudden event.
Here’s an important thing to keep in mind: Over 99% of these solar power systems are generally connected to the utility grid, which indicates the fact that if the grid goes down someday, the system will crash down as well.
In case you do have a battery backup solar system, you may stand a chance to run your system even after the EMP blast, provided there has been no damage done to the solar power system by the blast.
16. What Is Net Metering?
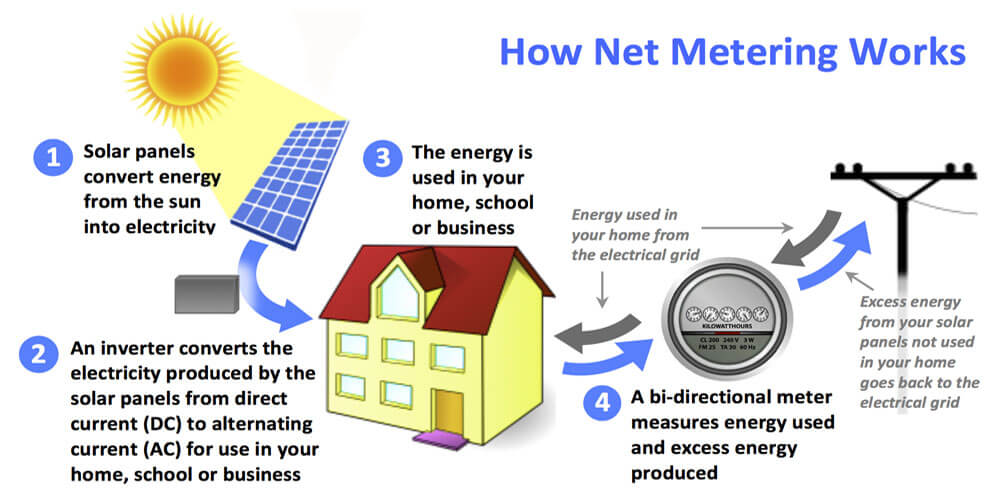
Well, several city grids, such as SDGE, offer a program to purchase the excess energy from your solar system. It is because most residences usually create excess energy that they require, making this an excellent option to invest in.
Therefore, net metering refers to a system where homeowners generate solar energy to remain connected to the utility grid and transfer the excess energy produced back to the utility grid. The respective utility company responsible offers to pay for this excess energy to offset other homeowners’ load.
These particular utility companies outline the terms and conditions that shape the agreement between the two of you to connect the excess energy to the grid. Understanding the net metering policies helps to figure out the kind of return a person may receive from their investment in solar power.
17. Will Solar Panels Save You Money?
Let’s be honest here; it’s not quite a fairytale as it may seem to be. Sometimes it can be hard to be satisfied with the price of solar panels when you’re indecisive about which kind to choose and what your preferences are.
For some perspective, your electricity bill might still be high even after installing solar panels. Whether solar panels will save you money or not depends on a few important factors. Firstly, you have to consider the federal solar tax credit.
The ITC allows for you to consider 26% of the annual cost spent on your solar system to apply it as a tax credit during the following year. Secondly, a PPA or a lease deal only offers to save very few bucks every month. You may find some more reliable literature of the federal solar tax credit in this article. On the other hand, a cash purchased system will genuinely put 100% of your power bill back into your savings.
18. Will Solar Power Become Cheaper?
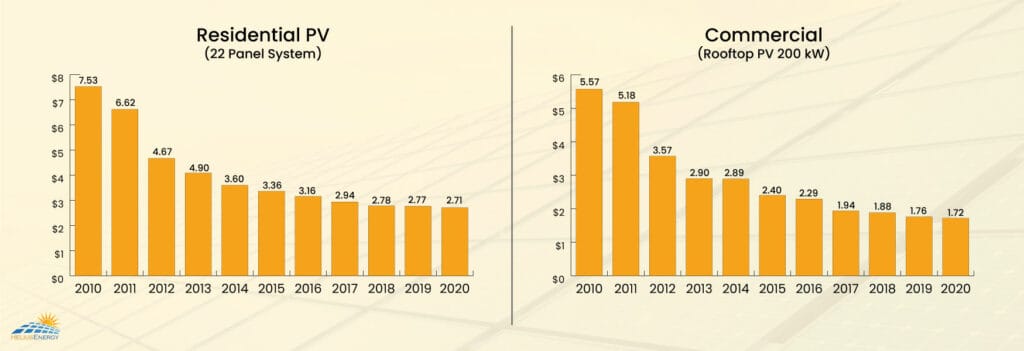
Fortunately, solar power pricing has been on a visible decline in recent past years. To estimate, prices have fallen almost over 89% as compared to where they were 20 years ago. Most manufacturers usually aim at achieving economies of scale and improvements in technology to organically reduce the pricing.
However, since the previous few years, the industry has visibly noticed an increase in pricing. The two biggest factors that are responsible for pricing increase are huge demand and a trade dispute that could result in tariffs on imported solar panels.
In addition to the increase in pricing on equipment, the 26% federal tax credit is scheduled to step down over the next few years till it expires in 2023. While a lot of different agents also go into the final price of a solar power system, the moral of the story is that there is really no incentive to wait anymore.
19. How Should You Finance Your Panels?
There are many ways to finance your solar panels. To begin with, some companies offer ownership packages that consist of cash or loan financing since it is considered the best way of manifesting control of the electricity while saving money simultaneously.
A few others offer Power Purchase Agreements or PPA as well as leasing deals that allow people to install a solar power system without paying money from their own savings.
However, the major problem with these deals is that people do not own their solar panels and are meant to pay the solar company for electricity.
These solar companies usually pump up the cost of electricity through price escalators every few years, cutting off any savings these people were once receiving. These solar companies also benefit from receiving all local and federal incentives like the Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for solar.
20. Are Solar Panels Worth The Money?
To answer that, it really depends on your personal preferences and decisions. However, several factors also depend on it:
1. The amount you have to pay for the utility per kilowatt-hour is undoubtedly one of the biggest reasons for considering whether or not to invest in solar power. In case the utility rate is higher, the payback period cuts short.
2. Well, not every roof is perfect for solar panel installation. If you have South, East, or West facing roof space that does not have shades, you’re good to go. However, if there are trees or other obstacles that provide shade to the whole area, solar power isn’t going to work.
3. With a solar power system, it’s almost the same as pre-paying your electricity costs for the next few years since you invest in a system that generally produces solar power for up to the following 30 years or more. The advantage here is that the cost of the system is much reduced.
Conclusion
Although solar power systems have been around for quite a long time now, there has been much confusion regarding its functionality and relative questions.
With the onset of this article with the sole purpose of solving major and interesting queries regarding solar power systems, many of you will now be able to explore more about solar energy and whether that’s what you want to opt for in the near future.






