Why do Solar Cells Need an Inverter?
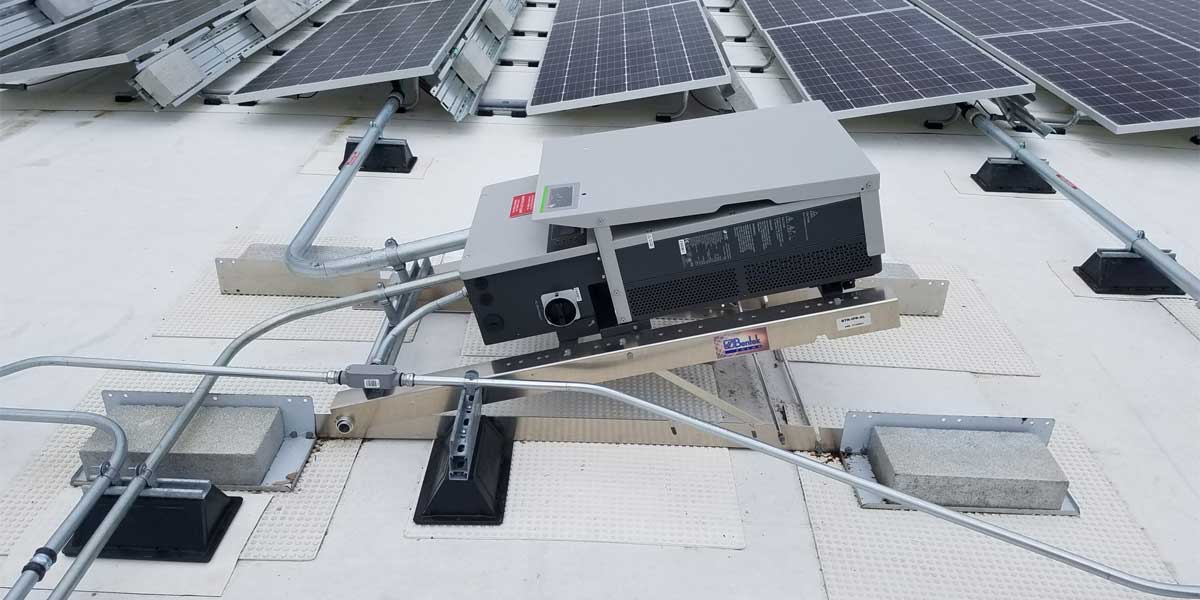

Most household equipment requires electricity in the form of alternating currents to function. Solar cells create electricity in the form of direct currents, which is why an inverter is required to convert electricity from DC to AC.
When the sun shines during the day, the solar cell absorbs this energy and produces a direct current, which in short form is DC. DC electricity is unsuitable for most modern appliances; this is the reason why solar cells need to convert it to a more usable form of electricity.
The process is termed as inverting, where one type of energy is converted into another type of energy. The DC type current is inverted to the more regularly utilized AC (alternating current). This is often for solar energy to be used inside a residence.
The job of conversion from AC to DC is done through an inverter. Solar cells provide DC electrical energy to it. The inverter then makes the DC input oscillate at a frequency by utilizing various electrical and electronic components. When the DC electricity from the solar cell is finally converted to AC, our home appliances can use it to function properly.
What are Solar Cells, and How do they Work?
A monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar cell is an electrical device placed in solar panels that converts light energy into electrical energy. This effect of producing electrical energy from light energy is known as the Photovoltaic effect.
In its most basic form, a solar cell is a p-n junction diode with electrical properties that change with exposure to sunshine. Solar cells are photovoltaic (PV) cells that produce DC electricity via the photovoltaic effect. When these cells are united, a solar module is formed.
Photovoltaic cells are made by way of semiconductors, one of the significant examples of which is silicon. The semiconductor material absorbs a portion of the light that strikes the cell, and the energy of the absorbed light is transmitted to it. Electrons are then knocked loose by the imparted energy, allowing them to flow freely.
Why do Solar Cells Produce Direct Currents?
Solar panels follow the same pattern as everyday batteries by producing direct currents. Direct current tends to be more consistent than alternating current, and solar cells can produce it without any additional electronics required to manage the electricity.
When sunlight strikes at the surface of a solar cell, it causes the electrons to flow, resulting in the generation of a current. These electrons will then flow in one direction.
An Unhindered single direction flow results in the generation of a DC. As a result, a solar cell produces only a DC form of electricity. This then warrants the use of an inverter which further converts the DC form to AC.
DC electricity may still be required on certain occasions. A smartphone would be a good example of this. Consider the USB cable that came with your smartphone.
It includes a cable that hooks into the phone’s port and a compact adaptor that fits into a standard wall outlet. Because a smartphone charger only requires 5V (volts), this converter converts AC to a lower voltage that may be used.
What is the Need to Convert DC to AC?
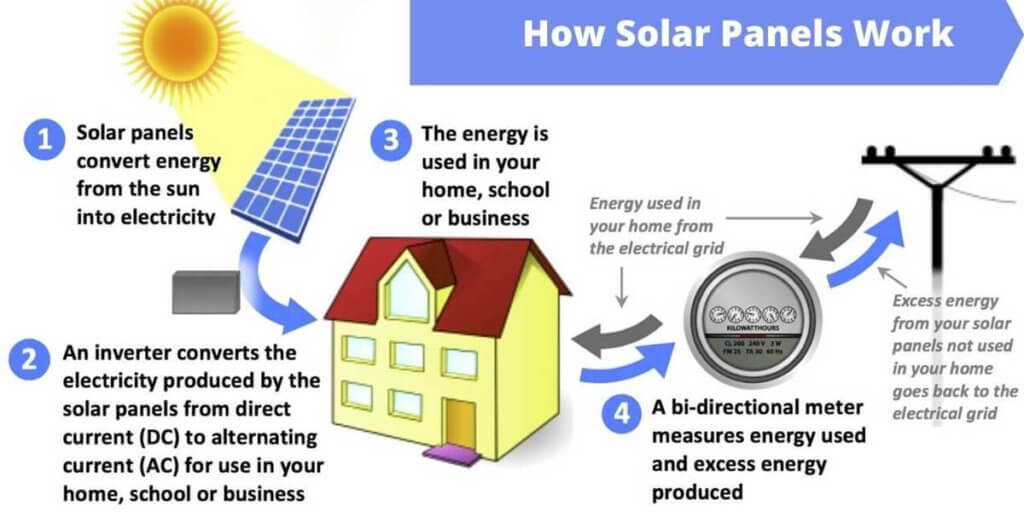
Why do solar cells need an inverter? Alternating current is used by the majority of our household outlets and appliances. They cannot be powered directly by direct current electricity. This is why, to benefit from solar energy, we must utilize an inverter.
Solar energy may be used to power our homes throughout the day using inverters. An inverter is a device that converts DC voltage and power into AC, allowing us to utilize our household equipment. When solar energy exceeds our household’s energy requirements, excess electricity is exported to the grid in the event of an on-grid solar power system.
The utility grid’s electricity is also in the type of AC. Under normal circumstances, to utilize your home appliances, you’ll need to receive electricity from a utility grid unless you decide to go off the grid completely.
Transmission and distribution lines are used to transport electrical energy from respective power facilities. These lines use high voltage and low current AC electricity to reduce electrical losses.
As a result, your solar panel system must adjust to your home’s AC power requirements. When you connect a solar system to the grid, you must also simultaneously coordinate its output power with the grid. This may be yet another reason why solar cells make use of an inverter.
What is an Inverter and How Does it Work?
In a solar energy system, an inverter is one of the most crucial components. It’s a gadget that transforms direct current (DC) power generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used by the electrical grid.
DC electricity is used to power several household appliances. On the other hand, many of the household appliances may be powered by an alternating current or AC.
Why do solar cells need an inverter? Our houses’ power sources are in the form of AC, which runs at conventional frequencies of 50Hz or 60Hz. In this case, the electricity changes direction 50 and 60 times per second, respectively. The bulk of our household gadgets uses this type of power to operate. The primary function carried out by an inverter is to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
If you plan on using solar energy to power your home, you must convert the solar cell’s output to AC. The capability of an inverter is also of worth in this particular situation. Solaredge and Enphase are some of the most popular solar inverters you can consider buying along with a solar panel home kit or a portable solar panel.
Can Solar Cells Work Without Inverters?
Home appliances require electricity to operate, which can be in the form of AC or DC. You may bypass the inverter element of your solar PV system if you just utilize solar energy for home appliances that require DC power.
Solar panels only generate the second type of power, DC. If you have DC-powered household equipment, your solar panels will continue to operate even without an inverter. They are most typically used at DC voltage values of 12, 24, or 48 volts.
Instead of utilizing an inverter, you may also connect your solar panels or cells to a charge converter. This is referred to as an off-grid configuration.
Verdict | Why do Solar Cells Need an Inverter?
In these modern times, both DC and AC electricity are required alternatively. While grids may run on alternating current, sensitive gadgets demand a more direct power supply. Solar energy from the sun is converted into DC electrical energy via solar cells. The DC power increases in capacity when the small solar cells are joined together, and the solar panel output capacity is released.
Solar panels in a series produce a substantial quantity of DC electrical energy, which is then sent into the inverter. After that, the inverter will convert it from DC to AC.
This is how solar cells and inverters function to power our alternating current electronics in the home. It also explains why solar panels require an inverter.
Solar cells provide an inverted power strategy, and since they are already commonplace, they will most likely continue to meet the needs of items like a 12V battery. The converter procedure can be advantageous and inefficient when seeking AC power, ranging from a single cell to a full-size solar panel.






